by Sarah Meisch
How State Lines are Drawn
Looking at a map of the United States, one spots a difference between the symmetrical states in the West and the more irregular borders of the East. At first glance, Colorado seems to have been easily drawn with its four clean borders. But why don’t we have the winding borders the eastern states have? Why are our mountains in the middle of the state, rather than drawn as a border? Is there a reason for the way our state cuts into part of Nebraska? This two-part series will address these questions and more, showing how the placement of Colorado’s state and territorial lines was part of a grander vision for political and cartographical harmony across the United States.
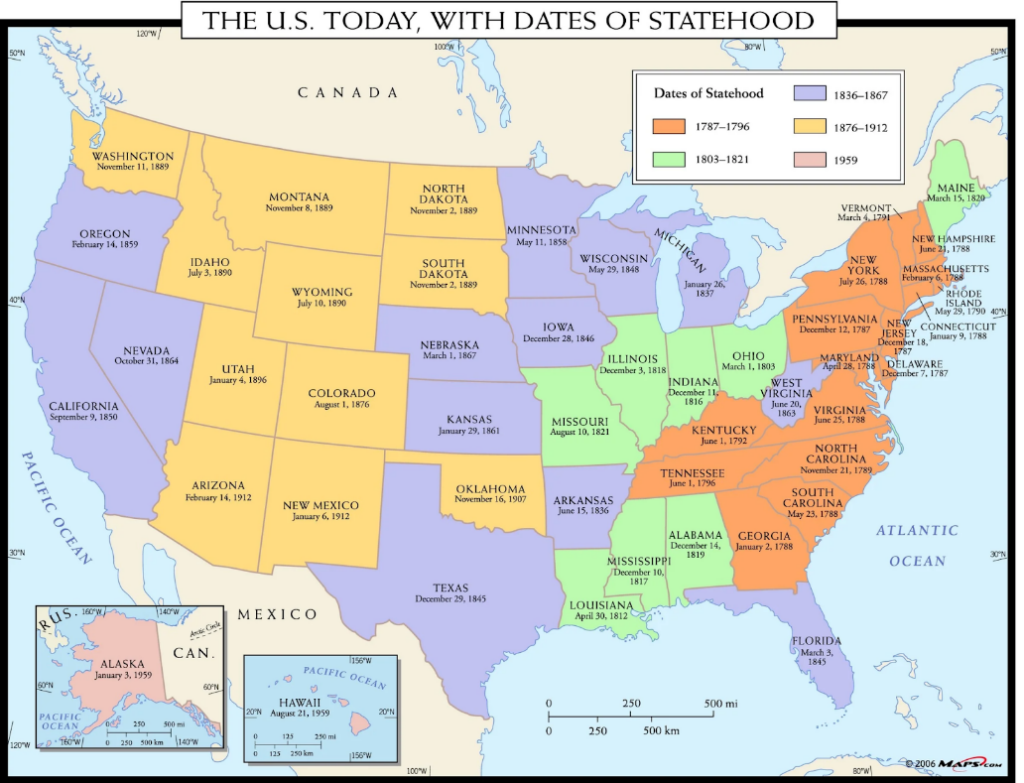
Throughout its history, the US has drawn its state and territorial borders according to geometry, with a focus on equity between the states and their resources. The Confederation government (1781-1789) solidified the Enlightenment-era precedent of drawing boundaries in straight lines through several ordinances in the 1780s, creating a distinct preference for geometry over geography. Most scholars of boundary-making have expressed disapproval of this approach, with historian James Bryce writing in the 1880s that state lines “are for the most part not natural boundaries fixed by mountain ranges, nor even historical boundaries due to a series of events, but purely artificial boundaries determined by an authority which carved the national territory into strips of convenient size.”
In the US, only part of a single state line follows a chain of mountains; this line lies along the Continental Divide dividing Idaho and Montana. Only one-third of states incorporate rivers into their boundaries, and outside of relatively small surveying errors, American states are generally neat and well-defined. It was always the intention of the US government to create cleaner boundaries based on straight lines, rather than borders based on unpredictable natural barriers. This explains the confusion over the state boundaries here in Colorado, as according to historian Derek Everett “geographically, there is no sensible reason for the state of Colorado to exist….[T]he simple rectangle that demarcates Colorado’s boundaries affords practically nothing…capable of bringing this disparate region into a single political entity.”[1]
However, in spite of the criticism aimed at geometric boundary-making, drawing lines based on geography has its drawbacks. Rivers are unreliable boundaries because they change dramatically over time; there have been several issues with the Missouri River as a boundary-maker over the years, as parts of Nebraska were found on the Missouri side of the river in the 1870s. Only the most entrenched and immovable rivers can realistically be used as boundaries, but these make up a very small portion of rivers. When the western states were being divided, there was a bit of public support for placing major rivers in the center of states instead to encourage riverine city and commercial development, but these petitions ultimately failed to convince Congress.
Mountain ranges as natural barriers are also difficult to use as state lines. It would be enormously difficult to survey a mountain range from peak to peak and cleft to cleft in all kinds of weather, even with modern technology. In the 1890s, scientist and explorer John Wesley Powell recommended state and county lines be drawn according to river basins, which are far less changeable over time than rivers, and also prioritize natural boundaries over geometric lines. There were many limitations with his plan for law enforcement and land ownership, and his suggestions came after the continental US had been divided up; therefore, it was too late to practically consider implementing Powell’s proposal.
Congress attempted to create equality between states, drawing lines in order for states to share access to water, agriculture, and maintain relative equality of size. States that are far larger than others, such as California, Texas, and Alaska, are states that created themselves. When Congress asked California and Texas to readjust their borders after admittance to the Union, few borders were actually altered, and the economic benefit of these states being part of the US outweighed the high risk of alienating them to preserve boundary equality.
Slavery was another integral piece of boundary making. To maintain an uneasy peace in the years leading up to the Civil War, the North and South would admit a slave-owning state when they would add a free state. This tit-for-tat division influenced the border placement of many states near the 36th and 37th parallels.
Even as new territories and states were in the offing, the US Congress had an eye on the future. Congress placed an emphasis on intentional planning, allowing for and encouraging the explosive growth in the West. The tapestry of our nation could very well have been checkered with states of different sizes, shapes, and names from what exist today, if it hadn’t been for the vision of equity and symmetry championed by our Enlightenment thinkers.
Stay tuned for Part 2 of this piece next week, which will explore the reasons behind Colorado’s borders, and how they have changed over time!
[1] Everett, “Creating the American West,” 11.
References
Abbott, Carl, Stephen J Leonard, and Thomas J Noel. Colorado: A History of the Centennial State. Fifth. Boulder, Colorado: University Press of Colorado, 2013.
American Library Association. “Indigenous Tribes of Colorado.” American Library Association, November 21, 2017. https://www.ala.org/aboutala/offices/denver-colorado-tribes.
“Articles of Confederation (1777).” National Archives and Records Administration. Accessed August 31, 2023. https://www.archives.gov/milestone-documents/articles-of-confederation#:~:text=The%20Articles%20of%20Confederation%20were,day%20Constitution%20went%20into%20effect
Berwanger, Eugene H. The Rise of the Centennial State: Colorado Territory, 1861-76. Urbana, Illinois: University Of Illinois Press, 2007.
Cengage. “Jefferson Territory | Encyclopedia.com.” www.encyclopedia.com. Accessed June 6, 2023. https://www.encyclopedia.com/history/dictionaries-thesauruses-pictures-and-press-releases/jefferson-territory.
Everett, Derek R. Creating the American West: Boundaries and Borderlands. Norman, Oklahoma: University of Oklahoma Press, 2014.
Frederic Logan Paxson. History of the American Frontier, 1763-1893. Cambridge, Massachusetts: The Riverside Press, 1924.
Geurts, Jennie. 2014. “How Rivers Shaped the Shape of Colorado.” Water Education Colorado. July 24, 2014. https://www.watereducationcolorado.org/publications-and-radio/blog/how-rivers-shaped-the-shape-of-colorado/.
Gower, Calvin. “Kansas Territory and Its Boundary Question, 1: ‘Big Kansas’ or ‘Little Kansas.’” Www.kshs.org 33, no. 1 (1967): 1–12. https://www.kshs.org/p/kansas-historical-quarterly-kansas-territory-and-its-boundary-question/13180.
History, Art & Archives: United States House of Representatives. “Draft Bill for Colorado Territory | US House of Representatives: History, Art & Archives.” history.house.gov. Accessed June 6, 2023. https://history.house.gov/HouseRecord/Detail/15032436207.
History Colorado. “Carving up a Continent: State Boundaries in the American West, Feat. Dr. Derek Everett.” www.youtube.com, October 5, 2021. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EUit0Mj5QH8.
History Colorado, and Michael Troyer. “Colorado Territory | Articles | Colorado Encyclopedia.” Coloradoencyclopedia.org, February 25, 2016. https://coloradoencyclopedia.org/article/colorado-territory.
Humeyumptewa, Aleks, and Tracie Etheredge. “An Inventory of the Records of Arapahoe County, Colorado.” Denver, Colorado: The Colorado Historical Society, 1994. https://www.historycolorado.org/sites/default/files/media/documents/2018/mss.00015_arapahoe_county_colorado.pdf.
“Is Colorado a Square State?” 2016. Denver Public Library History. August 1, 2016. https://history.denverlibrary.org/news/colorado-square-state.
Jacobs, Frank. “Colorado Is Not a Rectangle—It Has 697 Sides.” Atlas Obscura. Big Think, April 14, 2023. https://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/is-colorado-a-rectangle.
Library Of Congress, and Sponsoring Body Library Of Congress. Center For The Book. How the States Got Their Shapes. Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress, -07-15, 2008. Video. https://www.loc.gov/item/2021687996/.
Maness, Jack. “When Colorado Was Kansas, and the Nation Was (Even More?) Divided.” Denver Public Library, January 26, 2017. https://history.denverlibrary.org/news/when-colorado-was-kansas-and-nation-was-even-more-divided.
Paxson, Frederic. “The Boundaries of Colorado.” The University of Colorado Studies 2, no. 2 (July 1904).
Stein, Mark. How the States Got Their Shapes. New York: Smithsonian Books/Collins, 2008.
The U.S. Today, with Dates of Statehood Wall Map. Mapszu. Accessed June 6, 2023. https://cdn.shopify.com/s/files/1/0268/2549/0485/products/maps.com-the-u.s.-today-with-dates-of-statehood-wall-map_2400x.jpg?v=1572562951.
Trembath, Brian. “Jefferson Territory: The Renegade State That Almost Replaced Colorado.” Denver Public Library, June 24, 2020. https://history.denverlibrary.org/news/jefferson-territory-renegade-state-almost-replaced-colorado.
www.native-languages.org. “Colorado Indian Tribes and Languages.” Native Languages of the Americas. Accessed June 6, 2023. http://www.native-languages.org/colorado.htm.
Wikipedia. “Colorado Territory,” June 2, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colorado_Territory.
Wikipedia. “Four Corners,” May 7, 2023. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Four_Corners#:~:text=The%20Four%20Corners%20area%20is.
Zimmer, Amy. “Jefferson’s Legacy in Colorado.” www.coloradovirtuallibrary.org. Colorado Virtual Library, April 11, 2013. https://www.coloradovirtuallibrary.org/resource-sharing/state-pubs-blog/jeffersons-legacy-in-colorado/.

